Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that that mainly affects the lungs. This is a health condition that has plagued people since the ancient times. Tuberculosis is caused by two organisms namely Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Many people are suffering from this condition in different parts of the globe. Its cases have been on the rise since 1985 due to the high number of people who are infected with HIV. According to WHO, this is a health problem that affects nearly a third of the total world population. It was declared as a global emergency in 1993.
Primary Causes of Tuberculosis
In most instances, TB is passed from an infected to a healthy person via droplets. Tiny droplets of mucus or saliva are expelled to the surrounding air when an infected person talks, sneezes or coughs. Another person can get this disease by inhaling these tiny droplets.
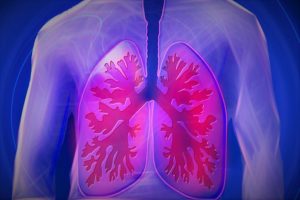
The infectious particles of TB reach the alveoli where they are engulfed by the TB bacteria known as the macrophage. Alveoli are the small saclike structures found in the lungs. The TB bacteria is then transmitted to the bloodstream and lymphatic system. This is how it is spread to the other organs. Further multiplication of the TB bacteria takes place in the body’s organs which have high oxygen pressures like the kidneys, the lung’s upper lobes, meninges, bone marrow among others. The patient is said to have TB once the bacteria causes clinically detectable disease.
Risk Factors for Tuberculosis
- Alcoholism
- HIV infection
- Crowded living conditions
- Low socioeconomic status
- Diseases that weaken your immune system
- Homelessness
- Health—care workers
- Migrating to areas or countries that have many cases
Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis
The symptoms of this disease are noticed at the advanced stages. The common symptoms include loss of energy, fever, night sweats, a productive cough, weight loss, and poor appetite.
When Should You Seek Medical Care or Treatment for Tuberculosis?
A close associate or family member who is suspected to have active TB should visit a doctor and get tested for TB. You should avoid getting into contact with such a person before he/she is treated. The affected patient is non-contiguous within the first few weeks. Patients who develop side effects after taking prescribed medications should call their doctors immediately. These side effects include visual changes, excessive fatigue, tiredness change in skin color, and itching.
Recommended Treatment Options for TB
Most of the TB patients are treated outside the hospital. Health practitioners seldom use surgery when treating patients. Instead, special medications are prescribed by doctors. Patients should take these drugs for about nine months. The treatment process takes a long time since the organisms that cause this disease to grow slowly and die slowly. Multiple medications are in treating resistant strains of TB.…

