Living with diabetes requires constant attention to lifestyle choices, and among these, physical activity plays a central role. Exercise is often underestimated, yet it has profound effects on cardiovascular health, blood sugar control and overall well-being. Whether you are newly diagnosed or have managed diabetes for years, integrating regular physical activity into your daily routine is vital. Beyond medication and diet, exercise helps the body utilize insulin more efficiently and reduces risks associated with complications. This article explores why regular exercise is crucial for managing diabetes, highlighting its top benefits and practical considerations. By understanding these advantages, you can approach your fitness plan with confidence and purpose.
Improves Blood Sugar Control
Exercise facilitate absorption of glucose by muscles absorb from the bloodstream, that reduces blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or strength training can have immediate and long-term effects on blood sugar control. Individuals with type 2 diabetes often see more stable glucose levels with consistent physical activity. For type 1 diabetics, monitoring blood sugar before and after exercise is important to prevent hypoglycemia, but exercise still contributes significantly to overall glucose management. By incorporating regular movement, diabetic patients can reduce reliance on medications while supporting their body’s natural ability to regulate sugar.
Supports Weight Management
Weight management is a vital factor in managing diabetes. Fat in excess, especially around the abdomen, contributes to insulin resistance, making blood sugar harder to control. Exercise burns calories and builds muscle, which increases metabolism and helps maintain a healthy weight. Combining cardiovascular exercises like jogging with resistance training maximizes fat loss and strengthens muscles, aiding glucose uptake. Maintaining a balanced weight improves insulin sensitivity and reduces strain on the heart and other organs, which are often vulnerable in diabetic patients. This benefit is especially significant for those with type 2 diabetes, where weight loss can have a major impact on disease progression.
Enhances Cardiovascular Health
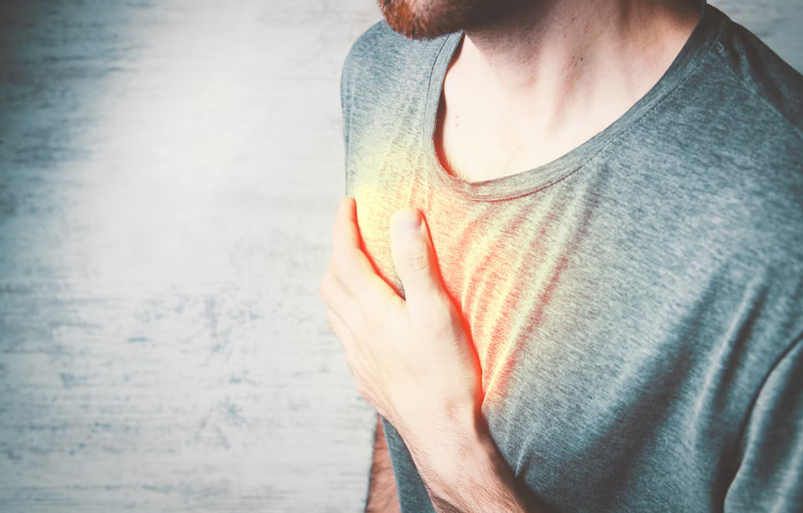

Diabetes increases possibility of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Regular exercise strengthens the heart, improve circulation, and reduces cholesterol levels, which collectively protect against cardiovascular complications. Activities like swimming, walking, or even light jogging improve heart function and help maintain healthy blood pressure. This reduces the likelihood of heart attacks and other complications associated with diabetes. For individuals managing diabetes, prioritizing cardiovascular health through exercise is a proactive step that contributes to both longevity and quality of life.
Boosts Mental Health and Reduces Stress
Managing diabetes can be mentally challenging, leading to anxiety or depression in some patients. Exercise stimulates release of endorphins and other mood-enhancing chemicals, reducing stress and promoting mental clarity. Regular physical activity also improves sleep quality, that has an effect on blood sugar levels and energy management. Mental well-being is linked to physical health in diabetes management, and exercise serves as a natural, effective tool to maintain emotional balance while supporting glucose regulation.
Reduces Risk of Long-Term Complications
Diabetes can lead to complications like neuropathy, kidney disease, and vision problems. Exercise enhances circulation, strengthens the cardiovascular system, and supports healthy weight, which together help prevent or delay these complications. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and reduces chronic inflammation, two major contributors to diabetic complications. By committing to regular movement, diabetic patients actively protect their organs and overall health, which is a crucial component of long-term disease management.
Regular exercise is critical in managing diabetes, giving benefits that extend far beyond calorie burning. The top five advantages include improved blood sugar control, better weight management, enhanced cardiovascular health, stronger mental well-being, and reduced risk of long-term complications. Incorporating consistent physical activity into daily routines empowers individuals with diabetes to take control of their health. Exercise complements medication, supports lifestyle changes, and provides a proactive approach to preventing complications. By understanding and embracing these benefits, diabetic patients can experience improved quality of life, better disease management, and a greater sense of confidence in handling their condition.